Authoritarian: A system where people are expected to obey all authority and rules, even though some of these rules and regulations may be unfair and cause the loss of personal freedom.
Clergy Priests or ministers of a religion that are usually a part of the Christian Church.
Constitution The system of laws and principles that a state, country or organisation is governed by.
Democracy A system of governance where people of a country can vote to elect their country’s representatives.
Enfranchisement The act of giving a person the right to vote in an election. Disenfranchisement means to take away the right to vote.
Enlightenment: The process of understanding something and helping other people to understand it. The Enlightenment Period was a period in the 18th century in Europe where scientists and writers argued that science and reasons should be more important than religion and tradition.
Fraternity: A group of people who share the same belief systems or interests or profession.
Government: A group of people who are responsible for leading a country or state.
Guillotine: These machines were usually used for the execution of prisoners or people who broke the law.
An image of a guillotine used to execute people. (Accessed on 25 May 2020). Image Source
Independence: A person can gain independence by achieving freedom and being able to make their own decisions. A country can gain independence by achieving freedom from the political control of another country.
Liberty: The state of being free from oppressive restrictions imposed by authority.
Natural Rights: Natural Rights refer to basic rights that include the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness.[1]
Nobleman: A man that is a member from a family that has a high social rank.
Oppression: The cruel and unfair treatment of people. This usually refers to an authority not giving some people the same freedom or rights as other people.
Parliament: A group of people who are elected to make and change the laws of a country.
Popular Sovereignty: A system where the sovereign power (ruling power) is entrusted and motivated by the people who chose the ruling power or government.[2]
Republic: A country that is governed by a president and politicians elected by the people and where there is no king or queen.
Revolution: An attempt, organized by a big group of people, to change the government of a country – usually by means of violence.
Social Classes: This refers to how people are placed in groups based on their social and/or economic status.[3]
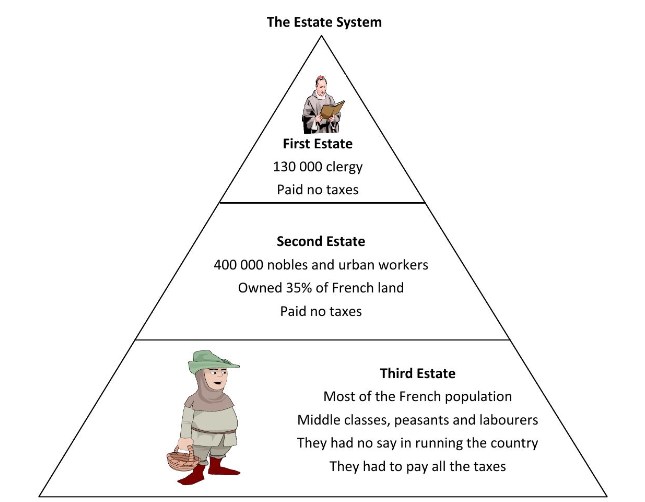 An illustration of the social structure of French society before the French Revolution. Image Source
An illustration of the social structure of French society before the French Revolution. Image Source
This article was originally produced for the SAHO classroom by
Ilse Brookes, Amber Fox-Martin & Simone van der Colff
[1] Study, “Natural Rights: Definition, Theory & Examples,” Study [online], available at https://study.com/academy/lesson/natural-rights-definition-theory-examples.html. (Accessed on 25 May 2020).
[2] Dictionary, “Popular Sovereignty,” Dictionary [online], available at https://www.dictionary.com/browse/popular-sovereignty. (Accessed on 25 May 2020).
[3] Britannica, “Social Class: Class Differentiation,” Britannica Encyclopaedia, [online], available at https://www.britannica.com/topic/social-class. (Accessed on 25 May 2020).